A Comprehensive Guide To Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System
What is HACCP? HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. It is a systematic preventive approach to food safety that is used to identify, evaluate, and control hazards that could occur in the production, storage, and distribution of food.
HACCP is based on the Codex Alimentarius, which is a collection of international food safety standards, guidelines, and codes of practice adopted by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC). The CAC is a joint program of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
HACCP is important because it helps to ensure that food is safe to eat. By identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards, HACCP can help to prevent foodborne illnesses, which can cause serious health problems and even death.
HACCP has been used in the food industry for over 30 years and has been shown to be effective in reducing the incidence of foodborne illnesses. HACCP is now a legal requirement in many countries, including the United States, the European Union, and Canada.
The HACCP system is based on seven principles:
- Conduct a hazard analysis.
- Determine the critical control points (CCPs).
- Establish critical limits for each CCP.
- Establish monitoring procedures for each CCP.
- Establish corrective actions for each CCP.
- Establish verification procedures.
- Establish documentation and record-keeping procedures.
HACCP is a complex system, but it is essential for ensuring the safety of our food supply.
HACCP
HACCP, or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, is a systematic preventive approach to food safety that is used to identify, evaluate, and control hazards that could occur in the production, storage, and distribution of food.
- Hazard identification: Identifying potential hazards that could occur in the food production process.
- Critical control point (CCP) determination: Identifying the points in the food production process where hazards can be controlled.
- Critical limit establishment: Establishing the maximum or minimum values that must be met at CCPs to prevent or eliminate hazards.
- Monitoring procedures: Establishing procedures to monitor CCPs and ensure that critical limits are met.
- Corrective actions: Establishing procedures to take corrective action when critical limits are not met.
HACCP is an important tool for ensuring the safety of our food supply. By identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards, HACCP can help to prevent foodborne illnesses, which can cause serious health problems and even death.
Hazard identification
Hazard identification is the first step in the HACCP process. It involves identifying all potential hazards that could occur in the food production process, from the receipt of raw materials to the dispatch of finished products.
- Biological hazards: These are hazards that are caused by microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Biological hazards can cause food poisoning, which can lead to serious illness or even death.
- Chemical hazards: These are hazards that are caused by chemicals, such as pesticides, cleaning agents, and heavy metals. Chemical hazards can cause a variety of health problems, including cancer, birth defects, and organ damage.
- Physical hazards: These are hazards that are caused by physical objects, such as glass, metal, and plastic. Physical hazards can cause injuries, such as cuts, punctures, and broken bones.
- Allergens: These are substances that can cause allergic reactions in some people. Allergens can be found in a variety of foods, including milk, eggs, peanuts, and shellfish. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe, and can even be life-threatening.
Hazard identification is an important step in the HACCP process because it allows food businesses to identify and control hazards that could pose a risk to consumers. By identifying hazards early in the food production process, food businesses can take steps to prevent or eliminate them, thereby ensuring the safety of their products.
Critical control point (CCP) determination
Critical control point (CCP) determination is a crucial component of HACCP. It involves identifying the points in the food production process where hazards can be controlled. CCPs are typically identified based on a hazard analysis, which identifies the potential hazards that could occur in the process and the points where those hazards can be controlled.
Once CCPs have been identified, critical limits must be established for each CCP. Critical limits are the maximum or minimum values that must be met at CCPs to prevent or eliminate hazards. Monitoring procedures must also be established to ensure that CCPs are operating within critical limits. Corrective actions must be established to take corrective action when critical limits are not met.
CCP determination is important because it allows food businesses to focus their resources on the points in the food production process where hazards are most likely to occur. By controlling CCPs, food businesses can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
For example, in a food processing plant, a CCP might be the temperature of the food during cooking. The critical limit might be 165 degrees Fahrenheit, which is the minimum temperature required to kill harmful bacteria. The monitoring procedure might be to measure the temperature of the food at regular intervals during cooking. The corrective action might be to adjust the cooking temperature or to re-cook the food if the temperature falls below the critical limit.
CCP determination is a complex process, but it is essential for ensuring the safety of our food supply. By identifying and controlling CCPs, food businesses can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
Critical limit establishment
Critical limit establishment is an essential component of HACCP. Critical limits are the maximum or minimum values that must be met at CCPs to prevent or eliminate hazards. Establishing critical limits is a complex process that requires a thorough understanding of the food production process and the hazards that could occur.
- Role of critical limits in HACCP
Critical limits play a vital role in HACCP by providing a clear target for monitoring and control at CCPs. By establishing critical limits, food businesses can ensure that hazards are controlled to an acceptable level and that food is safe for consumption.
- How critical limits are established
Critical limits are established based on a number of factors, including the nature of the hazard, the severity of the hazard, and the feasibility of controlling the hazard. Critical limits may be based on scientific data, regulatory standards, or industry best practices.
- Monitoring critical limits
Once critical limits have been established, they must be monitored on a regular basis to ensure that CCPs are operating within critical limits. Monitoring may be conducted using a variety of methods, such as temperature probes, pH meters, and visual observation.
- Corrective actions
If a critical limit is not met, corrective actions must be taken to bring the CCP back into control. Corrective actions may include adjusting the process, re-processing the food, or discarding the food. Corrective actions should be documented and reviewed to ensure that they are effective.
Critical limits are an essential component of HACCP. By establishing and monitoring critical limits, food businesses can ensure that hazards are controlled and that food is safe for consumption.
Monitoring procedures
Monitoring procedures are an essential part of HACCP. They ensure that CCPs are operating within critical limits and that hazards are being controlled. Monitoring procedures should be designed to be specific, measurable, accurate, and timely.
- Role of monitoring procedures in HACCP
Monitoring procedures play a vital role in HACCP by providing ongoing assurance that CCPs are operating within critical limits. By monitoring CCPs, food businesses can identify and correct any deviations from critical limits before they pose a risk to food safety.
- How monitoring procedures are established
Monitoring procedures should be established based on the specific hazards and CCPs identified in the HACCP plan. Monitoring procedures may include physical observations, chemical tests, or microbiological testing. The frequency of monitoring should be based on the risk associated with the hazard and the CCP.
- Recording and reviewing monitoring results
Monitoring results should be recorded and reviewed on a regular basis to ensure that CCPs are operating within critical limits. Monitoring results should be used to identify trends and make adjustments to the HACCP plan as necessary.
- Corrective actions
If a monitoring result indicates that a CCP is not operating within critical limits, corrective actions must be taken to bring the CCP back into control. Corrective actions may include adjusting the process, re-processing the food, or discarding the food. Corrective actions should be documented and reviewed to ensure that they are effective.
Monitoring procedures are an essential part of HACCP. By establishing and following effective monitoring procedures, food businesses can ensure that CCPs are operating within critical limits and that hazards are being controlled.
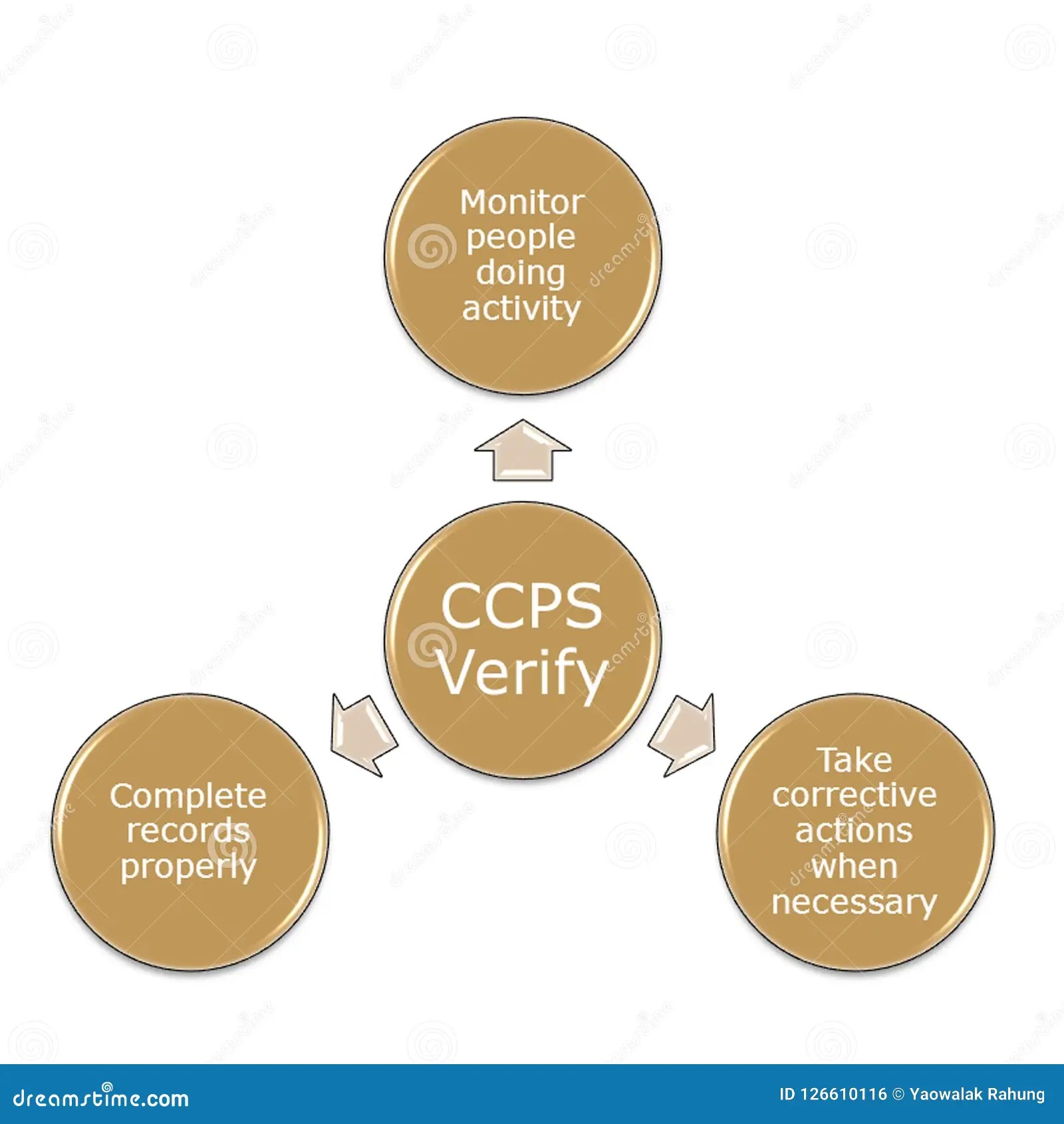
Corrective actions
Corrective actions are an essential part of HACCP. They ensure that when critical limits are not met, CCPs are brought back into control and hazards are eliminated or reduced to acceptable levels.
- Identification of deviations
The first step in taking corrective action is to identify that a deviation has occurred. This can be done through monitoring procedures, which should be in place to track CCPs and ensure that they are operating within critical limits.
- Determining the cause of the deviation
Once a deviation has been identified, the next step is to determine the cause. This can be done through a root cause analysis, which is a systematic process for identifying the underlying causes of a problem.
- Taking corrective action
Once the cause of the deviation has been determined, corrective action can be taken to bring the CCP back into control. Corrective actions may include adjusting the process, reprocessing the food, or discarding the food.
- Verifying that corrective actions have been effective
Once corrective actions have been taken, it is important to verify that they have been effective. This can be done through monitoring procedures, which should be in place to track CCPs and ensure that they are operating within critical limits.
Corrective actions are an essential part of HACCP. By establishing and following effective corrective action procedures, food businesses can ensure that CCPs are operating within critical limits and that hazards are being controlled.
HACCP FAQs
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic preventive approach to food safety that is used to identify, evaluate, and control hazards that could occur in the production, storage, and distribution of food.
Question 1: What are the benefits of HACCP?
HACCP has many benefits, including:
- Reducing the risk of foodborne illness
- Improving food safety
- Protecting consumers
- Increasing consumer confidence in the food supply
- Facilitating trade
Question 2: What are the key principles of HACCP?
The key principles of HACCP are:
- Conduct a hazard analysis.
- Determine the critical control points (CCPs).
- Establish critical limits for each CCP.
- Establish monitoring procedures for each CCP.
- Establish corrective actions for each CCP.
- Establish verification procedures.
- Establish documentation and record-keeping procedures.
HACCP is a complex system, but it is essential for ensuring the safety of our food supply.
Conclusion
HACCP is a systematic preventive approach to food safety that is used to identify, evaluate, and control hazards that could occur in the production, storage, and distribution of food. HACCP is based on the Codex Alimentarius, which is a collection of international food safety standards, guidelines, and codes of practice adopted by the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC). HACCP is important because it helps to ensure that food is safe to eat. By identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards, HACCP can help to prevent foodborne illnesses, which can cause serious health problems and even death.
HACCP has been used in the food industry for over 30 years and has been shown to be effective in reducing the incidence of foodborne illnesses. HACCP is now a legal requirement in many countries, including the United States, the European Union, and Canada.
Also Read
Article Recommendations

ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue8alppuZnKOyuL%2BQaJ%2Bam12YsLG%2FjaGrpqQ%3D