Ultimate Guide To AP Statistics Formula Sheet
In the world of statistics, having a reliable AP Statistics formula sheet is essential for students preparing for their AP exams. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a detailed overview of the most important formulas, concepts, and strategies needed to excel in AP Statistics. From understanding basic statistical terms to applying advanced techniques, this article covers everything you need to know to succeed. Alongside this, we’ll discuss the format of the AP Statistics exam and how to effectively utilize your formula sheet on test day.
As you prepare for your AP Statistics exam, having a well-organized formula sheet can be a game-changer. It serves as a quick reference that can help you recall essential formulas and concepts during the exam. This guide will not only provide you with the necessary formulas but also explain their applications, ensuring that you have a solid understanding of each one. By the end of this article, you will not only be equipped with a formula sheet but also the confidence to tackle any statistical problem that comes your way.
In addition to formulas, we will cover tips on how to create a personalized AP Statistics formula sheet tailored to your learning style. This will help reinforce your understanding and make studying more efficient. So, let’s dive into the essential formulas and concepts that you need to master for the AP Statistics exam!
Table of Contents
Introduction to AP Statistics
AP Statistics is a course that introduces students to the concepts and tools for collecting, analyzing, and drawing conclusions from data. It covers a variety of topics, including descriptive statistics, probability, statistical inference, and more. Understanding these concepts is crucial not only for passing the exam but also for applying statistics in real-world scenarios.
Basic Formulas in AP Statistics
Here are some fundamental formulas that are essential for AP Statistics:
- Mean (Average): \(\bar{x} = \frac{\sum{x}}{n}\)
- Median: The middle value of a data set when arranged in ascending order.
- Mode: The value that appears most frequently in a data set.
- Variance: \(s^2 = \frac{\sum{(x - \bar{x})^2}}{n-1}\)
- Standard Deviation: \(s = \sqrt{s^2}\)
Probability Formulas
Probability is a crucial topic in AP Statistics. Below are some key probability formulas:
- Probability of an Event: \(P(A) = \frac{\text{Number of favorable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of outcomes}}\)
- Complement Rule: \(P(A') = 1 - P(A)\)
- Multiplication Rule (Independent Events): \(P(A \cap B) = P(A) \times P(B)\)
- Addition Rule: \(P(A \cup B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A \cap B)\)
Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing
Confidence intervals and hypothesis testing are important aspects of statistical inference.
Confidence Intervals
- Confidence Interval for the Mean: \(\bar{x} \pm z\left(\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}\right)\)
- Confidence Interval for Proportions: \(\hat{p} \pm z\sqrt{\frac{\hat{p}(1 - \hat{p})}{n}}\)
Hypothesis Testing
- Null Hypothesis (H0): The hypothesis that there is no effect or difference.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H1): The hypothesis that there is an effect or difference.
- p-value: The probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the observed results, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is used to understand relationships between variables. Here are some key formulas:
- Linear Regression Equation: \(y = mx + b\)
- Correlation Coefficient (r): Measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables.
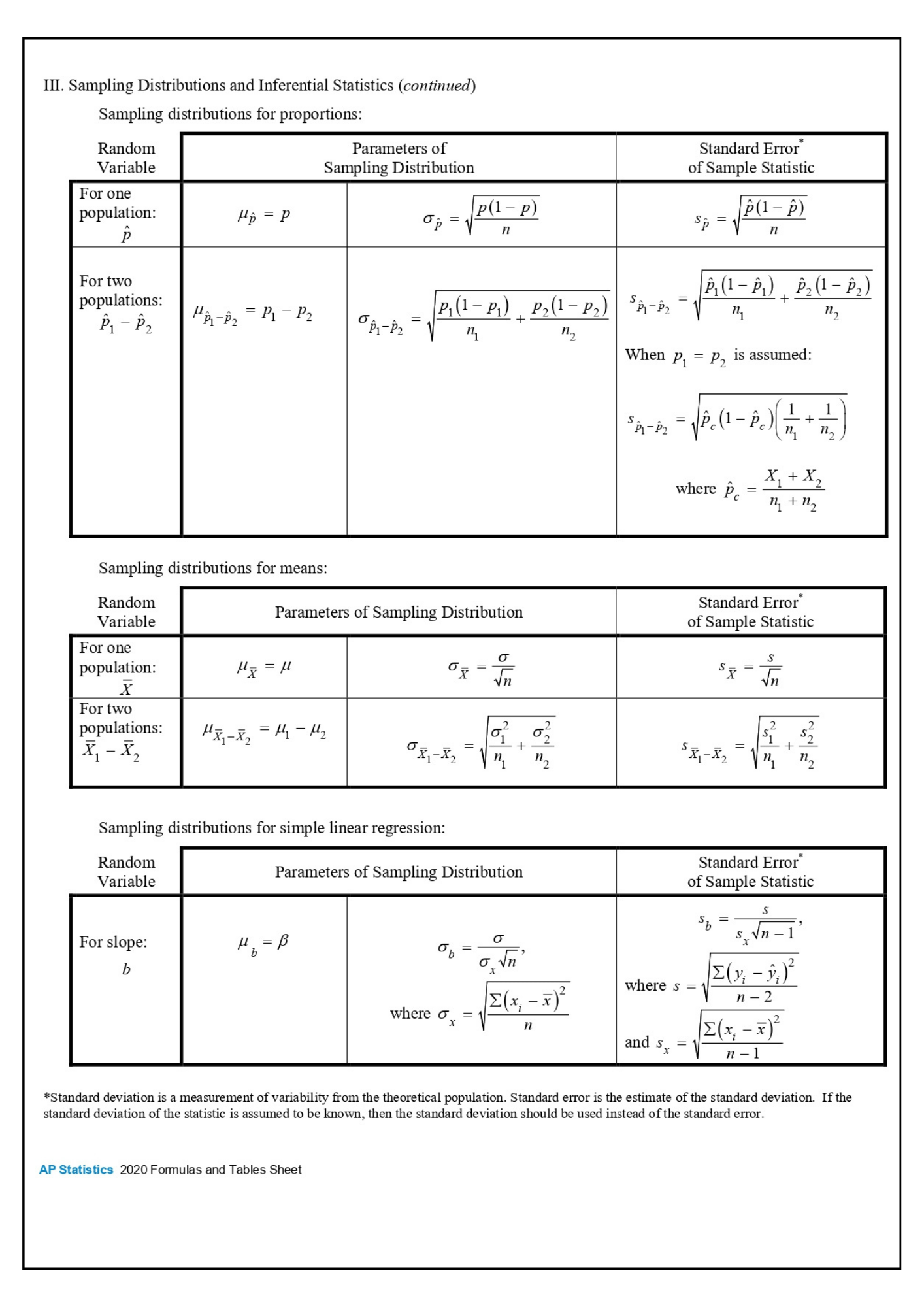
Sampling Distributions and Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem is a fundamental concept in statistics that states that the sampling distribution of the sample mean approaches a normal distribution as the sample size increases.
Data Interpretation Techniques
Understanding how to interpret data visually is crucial for AP Statistics. Techniques include:
- Histograms
- Box plots
- Scatter plots
Creating Your AP Statistics Formula Sheet
Creating a personalized formula sheet can enhance your study efficiency. Here are some tips:
- Include only the most relevant formulas that you struggle to remember.
- Organize formulas by topic for quick reference.
- Use color coding to differentiate between types of formulas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the AP Statistics formula sheet is vital for success on the exam. From basic statistics to advanced concepts like regression analysis and hypothesis testing, understanding these formulas will help you tackle a variety of problems. As you prepare for the exam, consider creating your own formula sheet that caters to your learning needs.
We encourage you to leave comments below or share this article with fellow students preparing for the AP Statistics exam. Remember, practice makes perfect, and with the right tools and resources, you can achieve your goals!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back for more insightful articles on statistics and other academic topics!
Also Read
Article Recommendations


ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9KtmKtlpJ64tbvKcGaaqF2owaLAyKyropujYrOwvsyuo5plo52ypsCNoaumpA%3D%3D