Understanding Its Importance And Applications
Boron atomic mass is a significant aspect of chemistry, playing a critical role in various scientific and industrial applications. This article will delve into the concept of atomic mass, specifically focusing on boron and its importance in different fields. Understanding boron’s atomic mass not only enhances our knowledge of chemistry but also highlights its applications in everyday life.
The atomic mass of boron is essential for chemists, researchers, and students alike. With a precise understanding of this element, one can better appreciate its behavior in chemical reactions and its role in compounds. Additionally, boron has a unique place in the periodic table, which merits closer examination. This article will explore boron’s atomic mass, its isotopes, and its broader significance in science and industry.
In this comprehensive guide, we will cover various aspects of boron atomic mass, including its definition, calculation, isotopes, and applications. We will also provide reliable references and statistics to support our findings. By the end of this article, readers will have a clear understanding of boron’s atomic mass and its significance.
Table of Contents
1. Definition of Boron Atomic Mass
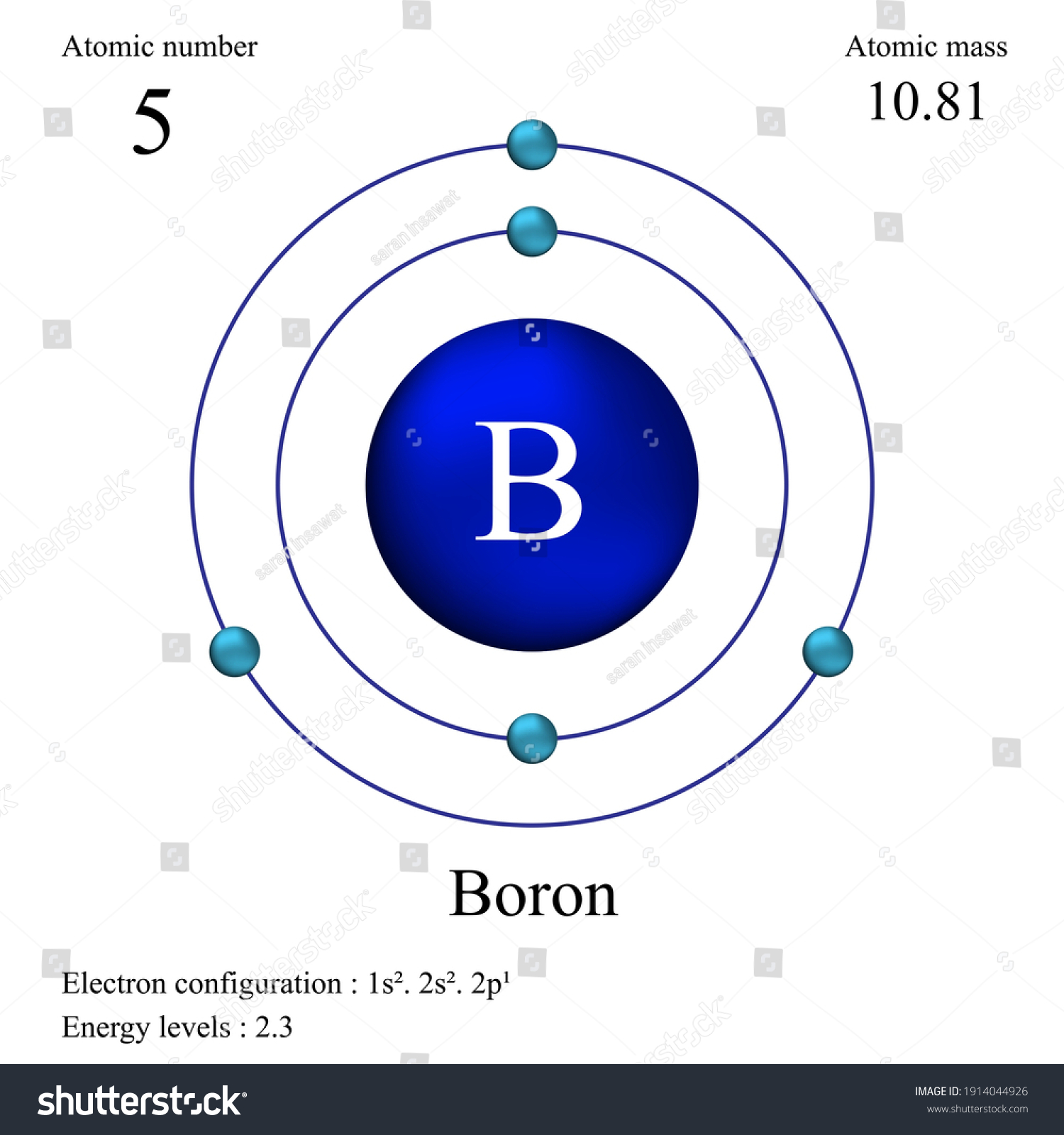
Boron atomic mass refers to the weighted average mass of the isotopes of boron in atomic mass units (amu). It is a crucial parameter in understanding how boron behaves in various chemical reactions. The atomic mass of boron is approximately 10.81 amu, which reflects the presence of its isotopes in nature.
2. Calculation of Boron Atomic Mass
The calculation of boron’s atomic mass involves accounting for the relative abundances of its isotopes. The formula used for this calculation is:
Atomic Mass = (fraction of isotope 1 × mass of isotope 1) + (fraction of isotope 2 × mass of isotope 2)
For boron, there are two stable isotopes: boron-10 and boron-11. Their respective masses and abundances are as follows:
- Boron-10: Mass = 10.012937 amu, Abundance = 19.9%
- Boron-11: Mass = 11.009305 amu, Abundance = 80.1%
Using these values, we can compute the atomic mass of boron accurately.
3. Isotopes of Boron
Boron has two stable isotopes: boron-10 and boron-11. In addition to these, there are several unstable isotopes, but they are not found in significant quantities. Understanding these isotopes is vital for various applications, especially in nuclear science and medicine.
3.1 Boron-10
Boron-10 has a lower atomic mass and is used primarily in neutron capture applications. This isotope plays a crucial role in nuclear reactors and radiation shielding.
3.2 Boron-11
Boron-11 is the more abundant isotope and is commonly used in the production of boron compounds, which have numerous applications in industry and agriculture.
4. Importance of Boron Atomic Mass
The importance of boron atomic mass extends beyond mere numbers. It affects the behavior of boron in chemical reactions and its interactions with other elements. Understanding boron's atomic mass is crucial for chemists and engineers working with boron compounds.
5. Applications of Boron in Industry
Boron and its compounds are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Agriculture: Boron is an essential micronutrient for plant growth and is commonly used in fertilizers.
- Glass Manufacturing: Boron is used to produce borosilicate glass, known for its thermal resistance.
- Metallurgy: Boron is used to improve the hardness and strength of metals.
- Nuclear Applications: Boron-10 is crucial in neutron capture for nuclear reactors.
6. Boron in Nature
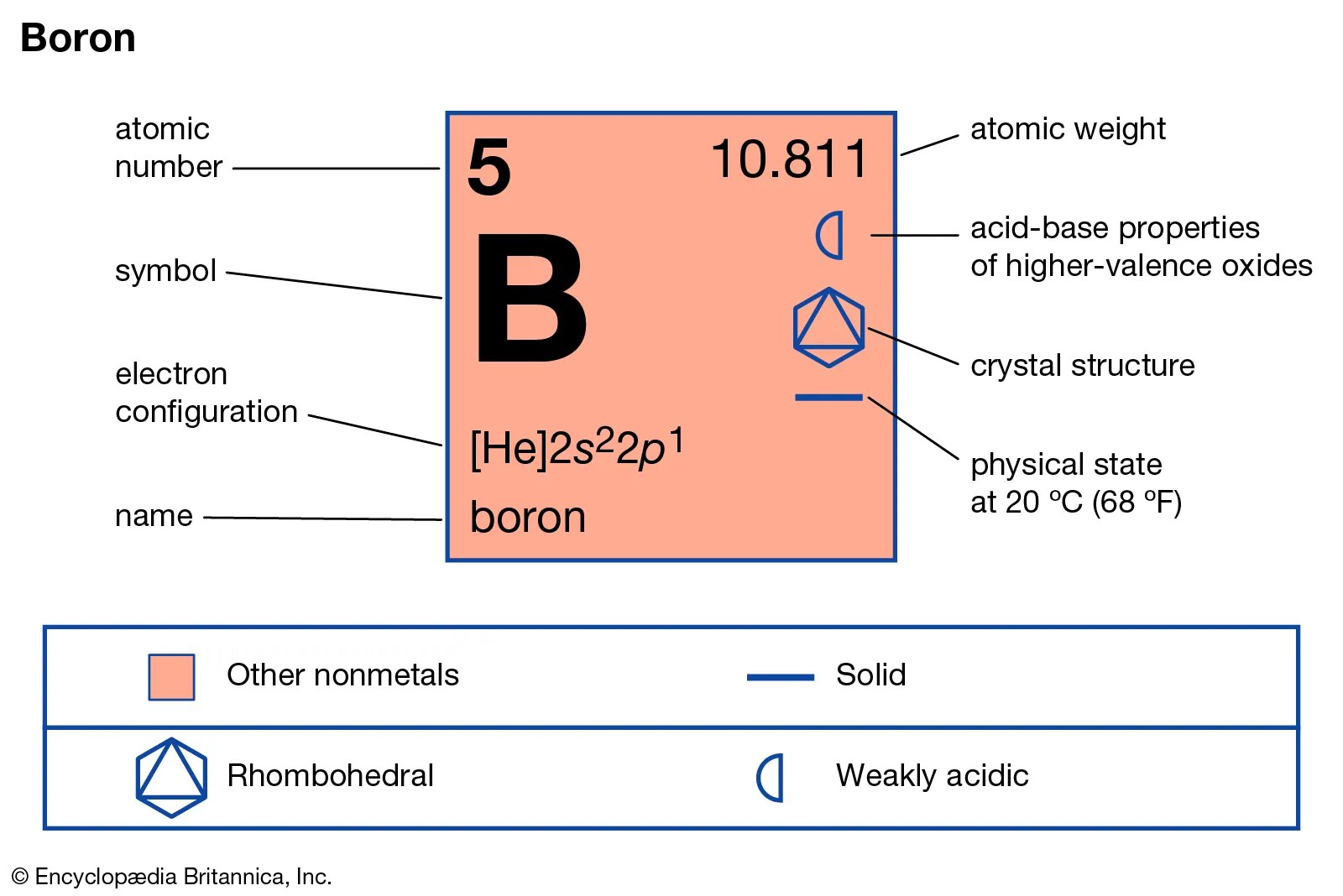
Boron is a naturally occurring element found in various minerals and compounds. It is primarily obtained from borate minerals, which are mined for industrial use. Below is a brief biodata of boron:
| Element | Boron |
|---|---|
| Symbol | B |
| Atomic Number | 5 |
| Atomic Mass | 10.81 amu |
| Electronegativity | 2.04 |
7. Conclusion
In summary, understanding boron atomic mass is essential for various scientific and industrial applications. Its isotopes, boron-10 and boron-11, contribute to its unique properties and uses. From agriculture to nuclear applications, boron plays a vital role in our daily lives. We encourage readers to explore more about boron and its applications.
8. Sources and References
- Periodic Table of Elements
- American Chemical Society
- Journal of Chemical Education
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Also Read
Article Recommendations
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9KtmKtlpJ64tbvKcGabp6Kku26t06ikoptdoq60v42hq6ak