Understanding Lake Profile Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
Lake profile zones are essential components of aquatic ecosystems, influencing everything from biodiversity to water quality. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of lake profile zones, their significance, and how they interact with the environment. Understanding these zones is not only vital for ecologists and environmental scientists but also for anyone interested in the health of our water bodies.
As we delve into the realm of lake profile zones, we will categorize them according to their distinct characteristics, functions, and the organisms that inhabit them. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide valuable insights into the ecological and hydrological dynamics at play within lake systems.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply an enthusiast, this article aims to shed light on the importance of understanding lake profile zones and their role in maintaining ecological balance. Let’s embark on this informative journey!
Table of Contents
What Are Lake Profile Zones?
Lake profile zones refer to the distinct areas within a lake that exhibit unique physical and biological characteristics. These zones are primarily defined by factors such as depth, light penetration, temperature, and the types of organisms that inhabit them. Understanding these zones is crucial for studying lake dynamics, as they influence nutrient cycling, energy flow, and habitat availability.
The concept of lake profile zones is essential for ecologists, hydrologists, and environmental managers. By examining these zones, researchers can gain insights into the overall health of a lake, assess biodiversity, and monitor changes within the ecosystem over time.
The Different Types of Lake Zones
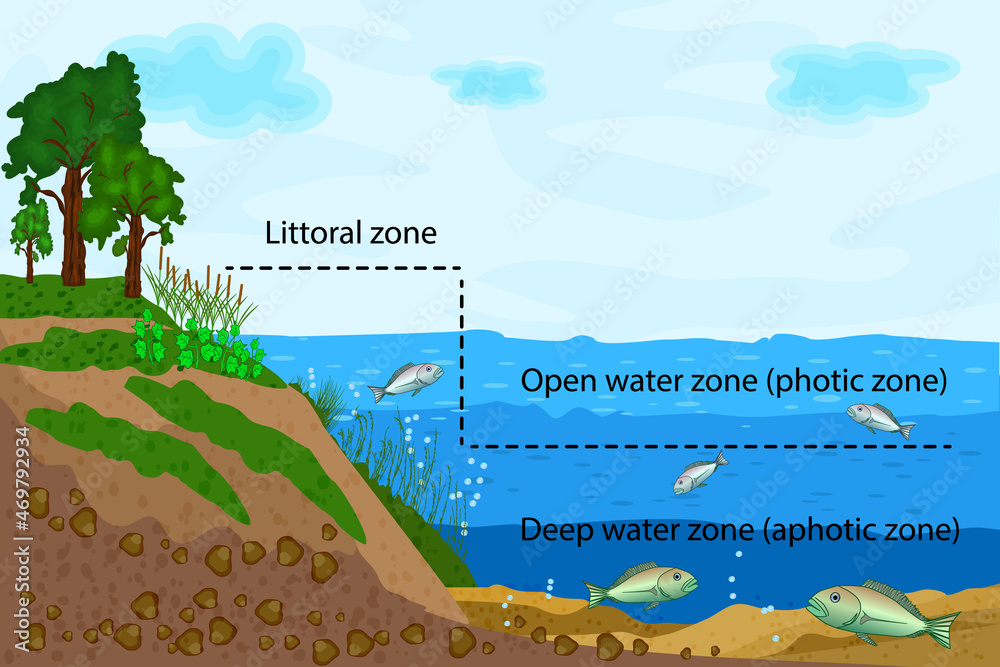
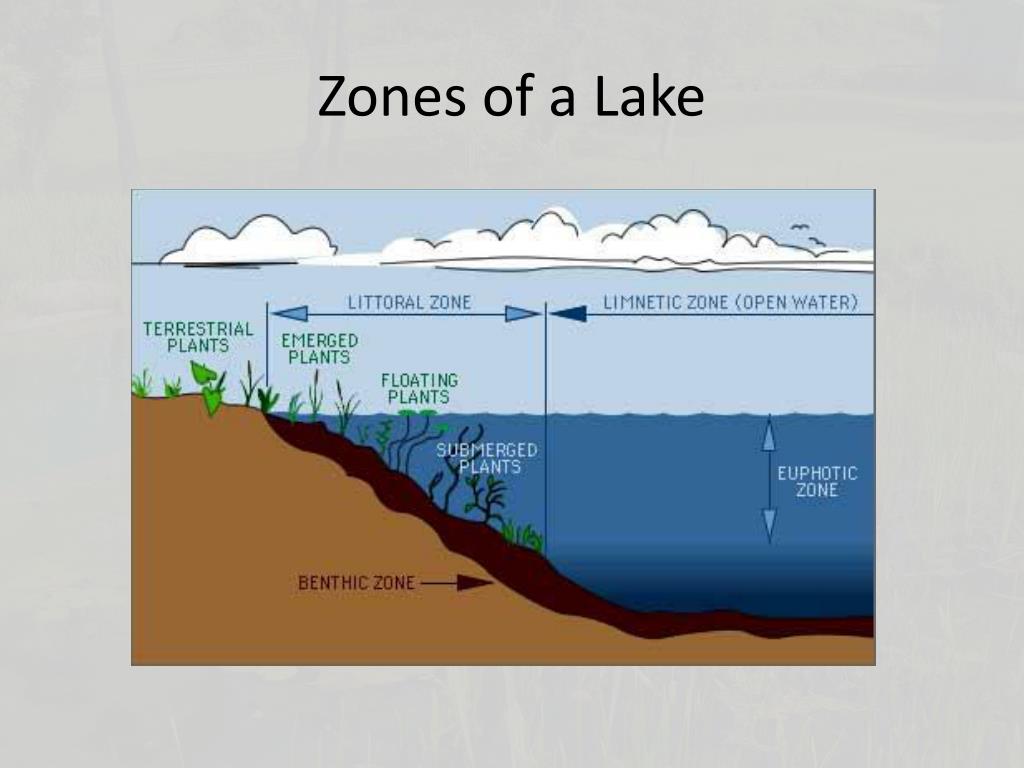
Lake profile zones can be broadly classified into four main categories: the littoral zone, limnetic zone, profundal zone, and benthic zone. Each of these zones has its own unique characteristics and plays a vital role in the overall functioning of the lake ecosystem.
1. Littoral Zone
The littoral zone is the shallow area of a lake where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, allowing for the growth of aquatic plants. This zone typically extends from the shoreline to a depth where light can no longer support photosynthesis. Key features of the littoral zone include:
- Rich biodiversity of plant and animal life
- Habitat for fish spawning and nursery areas
- High nutrient levels, supporting various trophic levels
2. Limnetic Zone
The limnetic zone is the open water area of a lake that is well-lit and extends to the depth where light can still support photosynthesis. This zone is characterized by:
- Presence of phytoplankton and zooplankton as primary producers
- Habitat for various fish species
- Higher oxygen levels compared to deeper zones
3. Profundal Zone
The profundal zone is the deep, dark area of the lake where light cannot penetrate. This zone is typically cooler and has lower oxygen levels. Key characteristics include:
- Decomposition of organic matter from upper zones
- Home to specialized organisms adapted to low-light conditions
- Lower biodiversity compared to the littoral and limnetic zones
4. Benthic Zone
The benthic zone refers to the bottom of the lake and includes sediments and organic matter. This zone is crucial for nutrient recycling and supports various organisms, including:
- Decomposers such as bacteria and fungi
- Invertebrates that play a role in sediment turnover
- Fish species that feed on benthic organisms
The Role of Lake Profile Zones in Ecosystems
Lake profile zones play a critical role in maintaining the ecological balance of aquatic systems. Each zone contributes to the overall productivity and health of the lake in various ways:
- Nutrient cycling: Different zones facilitate the movement and transformation of nutrients necessary for supporting life.
- Habitat diversity: By providing varied habitats, lake zones support a wide range of species, enhancing biodiversity.
- Food webs: Each zone supports different trophic levels, contributing to complex food webs that are essential for ecosystem stability.
Factors Influencing Lake Profile Zones
Several factors influence the characteristics and dynamics of lake profile zones, including:
- Climate: Temperature and precipitation patterns affect water levels and thermal stratification.
- Geology: The physical characteristics of the lakebed influence sediment composition and nutrient availability.
- Human activity: Urbanization, agriculture, and pollution can significantly alter lake zones and their functions.
Human Impact on Lake Zones
Human activities have profound effects on lake profile zones. These impacts can lead to:
- Eutrophication: Excessive nutrient runoff can lead to algal blooms, affecting water quality and oxygen levels.
- Habitat destruction: Development and pollution can degrade habitats, reducing biodiversity.
- Climate change: Altered temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the natural balance of lake zones.
Conservation Efforts for Lake Zones
To protect and preserve lake profile zones, various conservation strategies are being implemented, including:
- Restoration projects: Efforts to restore degraded habitats and improve water quality.
- Pollution control: Implementing regulations to reduce nutrient runoff from agricultural and urban areas.
- Public education: Raising awareness about the importance of lake ecosystems and the need for conservation.
Future Research Directions
As our understanding of lake profile zones evolves, future research may focus on:
- Impact of climate change on lake dynamics and biodiversity
- Long-term monitoring of lake health and water quality
- Innovative conservation strategies to mitigate human impacts
Conclusion
In conclusion, lake profile zones are vital components of aquatic ecosystems that contribute to biodiversity, nutrient cycling, and habitat diversity. Understanding these zones is essential for effective management and conservation efforts. As stewards of our environment, it is our responsibility to protect these invaluable resources for future generations. We encourage readers to engage with their local ecosystems, contribute to conservation efforts, and stay informed about the health of lakes in their communities.
We invite you to leave your thoughts in the comments section below, share this article with others, or explore more on our site about the fascinating world of aquatic ecosystems.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more insightful articles in the future!
Also Read
Article Recommendations

ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7tMHRr6CvmZynsrS71KuanqtemLyue9WiqZqko6q9pr7SrZirq2lkuaK3xGanq6eWnrmmedmopZ6rXp3Brrg%3D